Umbilical Artery Doppler Reference Ranges
The calculator estimates the 50th and 95th percentile values for commonly used umbilical artery impedance indices (S/D ratio, resistance index, and pulsatility index) based on gestational age.
Umbilical artery (UA) impedance indices are calculated by using ultrasound to measure the blood flow waveforms from the umbilical arteries through a free-floating portion of the umbilical cord.
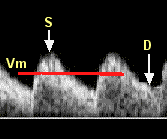
S = systolic peak (maximum velocity); the maximum velocity during contraction of the fetal heart.
D = end-diastolic flow; continuing forward flow in the umbilical artery during the relaxation phase of the heartbeat.
Vm = mean velocity.
The ratios (indices) of resistance to blood flow (impedance) are calculated as:
S/D ratio = systolic velocity ÷ diastolic velocity
Resistance index (RI) = (systolic − diastolic) ÷ systolic
Pulsatility index (PI) = (systolic − diastolic) ÷ mean velocity
In the normal fetus, resistance to flow (impedance) decreases in the umbilical artery due to increasing numbers of tertiary stem villi as the placenta matures.
Calculator
Reference ranges established for approximately 19–41 weeks at a free-loop segment of the umbilical cord [2].References
- Gosling RG, et al. The quantitative analysis of occlusive peripheral arterial disease by non-intrusive ultrasound technique. Angiology. 1971;22:52–5. PMID:5101050
- Acharya G, Wilsgaard T, Berntsen GKR, Maltau JM, Kiserud T. Reference ranges for serial measurements of umbilical artery Doppler indices in the second half of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192:937–44. PubMed